
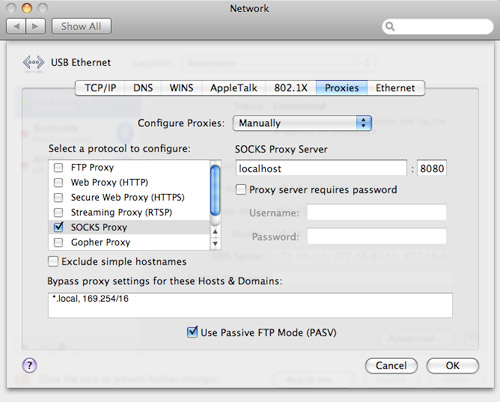
Pass in proto tcp from any to any port 60022 Rdr pass inet proto tcp from any to any port 60022 -> 127.0.0.1 port 22 I've tried using pfctl to set up forwarding: $ echo " I've tried unsuccessfully adapting these Ubuntu instructions to the Mac. And how do I get macOS to even start listening on port 60022?
#Mac ssh server port how to#
If it's supposed to happen in the server, I don't understand how to do that. Is this something that I should do in the router, or in the local server? The router's "Port Range Forwarding Table" config does allow packets of a given port range to be forwarded to a particular IP, but it doesn't appear to allow me to translate from one port to another. I don't understand how to forward traffic from port 60022 to 22. I now want to be able log in through another port (let's say 60022) like so: $ ssh -p 60022 I have successfully configured my router ( Cisco RV325, which has a fixed WAN IP address of, say, 99.99.99.99) so that I can log in remotely to the server (at static LAN IP address 12.0.0.123) on port 22, like so: $ ssh -p 22 ( I hear that it improves security to use a port other than the default. The solution is to open the browser locally, and to route the traffic between the browser and the jupyter notebook server running on deeplearning, through portal.I want to do remote ssh logins from outside my network to a server (macOS Sierra) on my LAN, using a port other than 22. If your local network connection is slow, the browser will feel slow and unresponsive. These incompatibilities make the remote graphics applications sluggish even on very fast networks. And that's clearly the case here since we want to make use of nvidia GeForce GPUs for deep learning.
#Mac ssh server port drivers#
If local runs macOS, there are incompatibilities between the X11 on deeplearning and the one on the mac, when nvidia drivers are used on deeplearning.

This does work because we used ssh with the -X option, which enables X11 forwarding, and thus makes it possible to open graphics application remotely. This opens a browser on deeplearning, and displays the browser window on local. In this situation, what most physicists would do is the following:Ĭonnect from the local to portal with ssh -XĬonnect from the portal to deeplearning with ssh -X That's a fairly typical configuration in research labs and companies. Portal is on the lab network, and is also visible from outside. This machine is inside the lab network and is not accessible from outside, but I have ssh access to it from inside. The computers involved are the following:ĭeeplearning is the deep learning station. I only try to find ways to do data science efficiently, and I hope I can help you with that as well. Therefore, the terminology I'm using may be incorrect. Afterwards, you'll need only a couple seconds to set up the connection with your remote jupyter notebooks.īefore we get started, please keep in mind that I'm just a physicist with limited knowledge of networking.
It might take you 10 minutes to set everything up the first time, but it's worth it. Start a jupyter notebook server on this machineĬonnect to this server from a browser running on your local machine to create and use jupyter notebooks

In this post, I'd like to show how I proceed to create and use jupyter notebooks on a remote machine.Ĭreate an ssh tunnel to a remote machine behind a firewall Still, quite often, I either don't have time to commute to the lab and just work from home, or I'm at CERN, 200 kms away. Unfortunately, it's behind a firewall and is not directly accessible from outside. It's quite nice, with 20 cores, 64 GB RAM, a large amount of SSD disk space for my data, and most importantly two GeForce GTX 1080 Ti. I've got a linux machine dedicated to deep learning development in my lab.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
